Audi Scales AI in Automotive Production With Edge Cloud
Audi AG continues to expand its use of AI in automotive production and logistics. The company scales its own cloud platform for production and introduces new AI use cases and technologies for large-scale series production. Audi combines decades of manufacturing expertise with smart digital solutions and draws on strong partnerships to accelerate progress.
“Artificial intelligence is a quantum leap for efficiency in our production. With the digitalisation roadmap, we are transforming our plants into smart factories where AI acts as a partner, providing our employees with tailored support. The first AI-controlled robots are taking over ergonomically strenuous tasks, and chatbots are providing additional relief,” explains Gerd Walker, Member of the Board of Management for Production and Logistics at Audi AG. “We are bringing together Audi’s decades of production expertise, our own innovative strength, and the expertise of strong partners such as the Innovation Park Artificial Intelligence (IPAI) in Heilbronn.”
Audi puts Edge Cloud 4 Production (EC4P) into operation across its production environment. With this step, the company sets a new benchmark in fully networked factory automation and lays the foundation for broader AI adoption in production. EC4P combines conventional automation technology with cloud flexibility and computing power. Audi uses that combination to simplify processes, reduce on-site hardware, and roll out new functions faster. This stabilises processes, cuts maintenance costs, and strengthens IT security.
Audi already centrally guides workers in vehicle assembly at its German plants via the cloud. Employees on the production line receive information such as vehicle specifications or regional versions from a central source in real time. The shift to the cloud has removed the need for more than 1,000 industrial PCs.
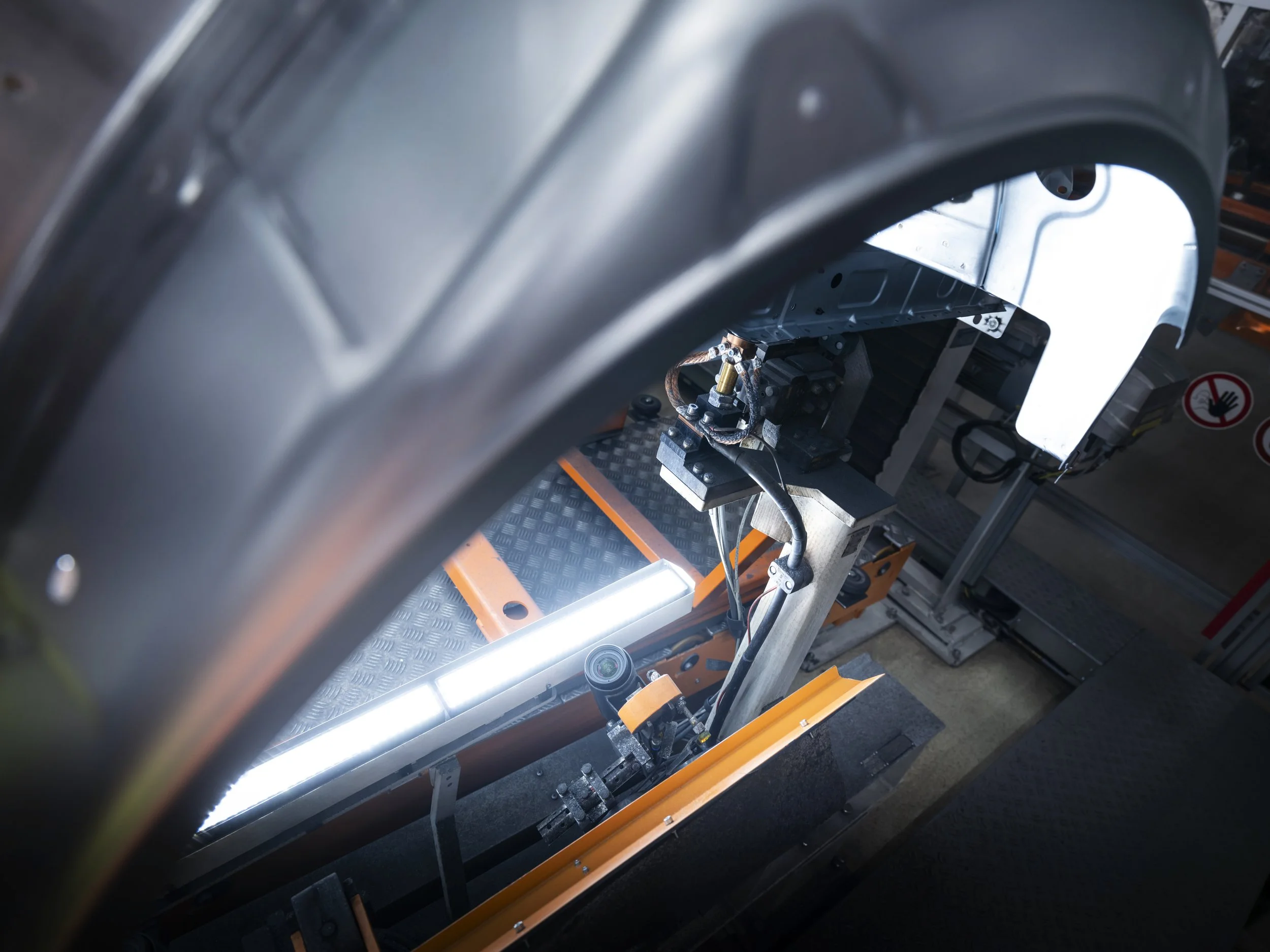
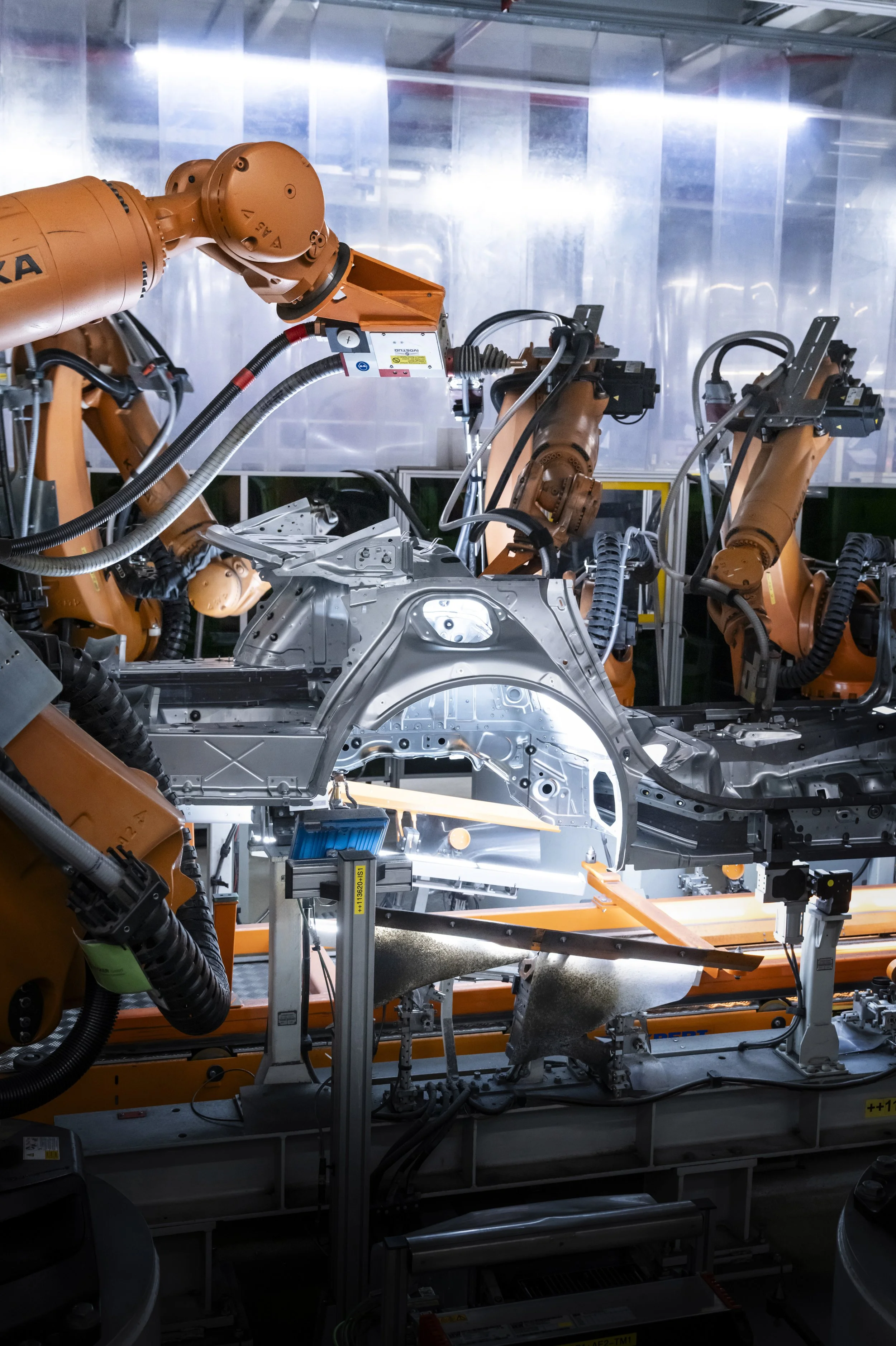
At the Neckarsulm body shop for the A5 and A6 series, Audi now uses EC4P in a highly automated environment for large-scale series production. Virtual programmable logic controllers (vPLC) replace local hardware controllers on the production lines. Industrial devices, including around 100 robots, coordinate through EC4P with millisecond precision. EC4P meets demanding requirements for smooth series production and enables teams to manufacture several hundred vehicle bodies per day across three shifts. Audi says the industry has not matched this benchmark to date.
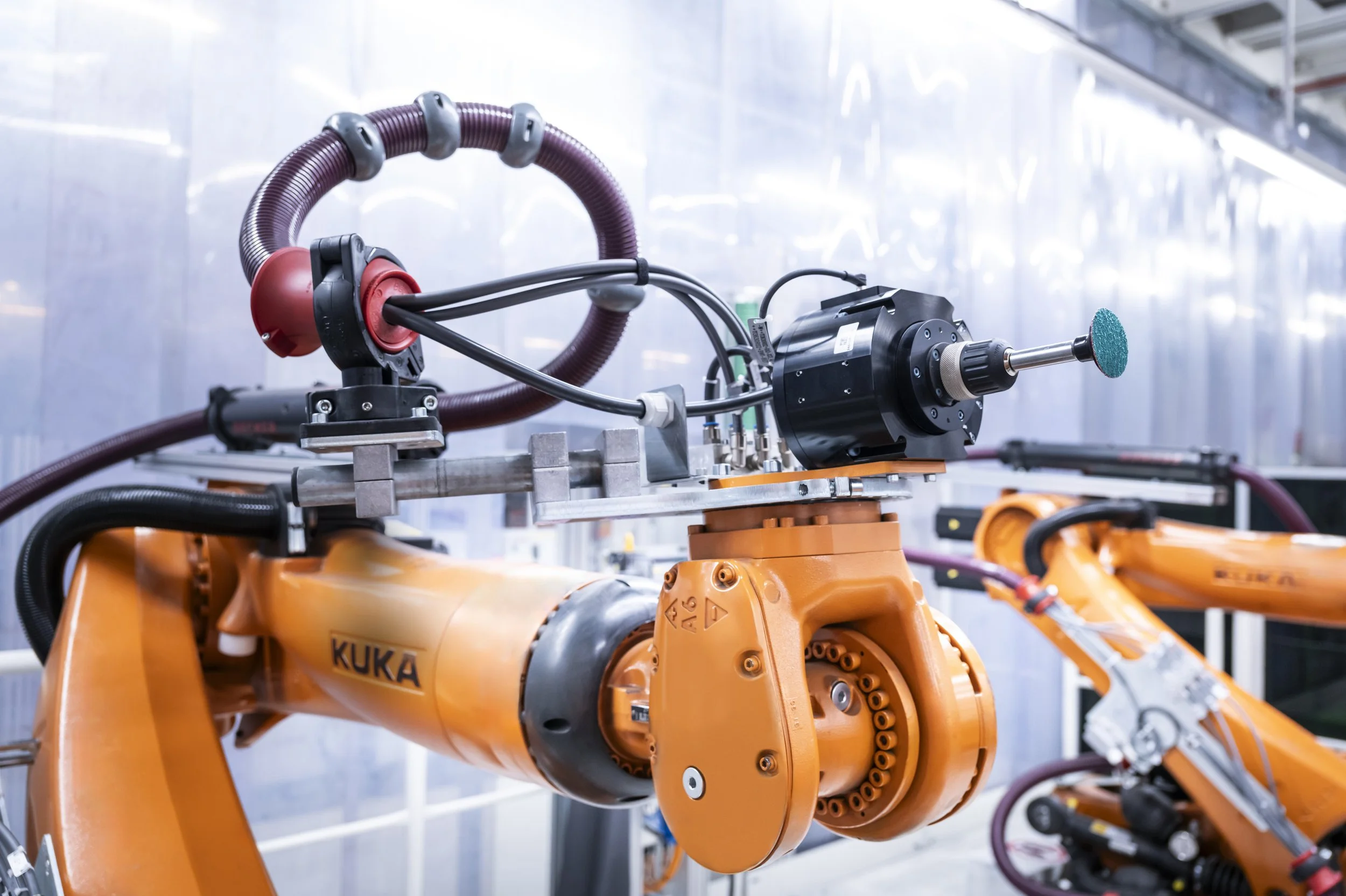
Audi will run the Weld Splatter Detection (WSD) system on EC4P in the future, adding flexibility and scalability. At Audi’s Neckarsulm site, WSD detects weld splatter on the underbody of a car body and marks it with light. A recent upgrade enables a robot arm to grind down the splatter, removing a physically demanding task from employees. Audi will soon bring the Volkswagen Group's first AI-supported weld spatter detection system into series production at six plants in Ingolstadt.
Audi also develops ProcessGuardAI, an in-house AI solution that monitors manufacturing processes. Audi data experts made this possible when they built the cross-plant “P-Data Engine” platform over the past few years. The platform consolidates system and plant data from production at a consistent quality level. With this database, Audi data scientists can develop and scale AI applications more quickly and efficiently, including ProcessGuardAI. The module standardises decades of expert knowledge with plant and process data and supports scalable use across the Volkswagen Group.
ProcessGuardAIn already monitors production steps in real time using machine and sensor data. It spots anomalies early and alerts experts. The Neckarsulm paint shop is now running a pilot for two use cases, including pretreatment optimisation and anomaly detection in cathodic dip coating (CDC). Audi plans to introduce series production in the second quarter of 2026. Early fault detection reduces manual work steps and lowers follow-up costs. In the next stages, ProcessGuardAIn will provide data-based recommendations and guide employees step by step through an app. Over time, Audi expects ProcessGuardAI to support predictive maintenance and quality assurance across plants by monitoring manufacturing processes end-to-end.
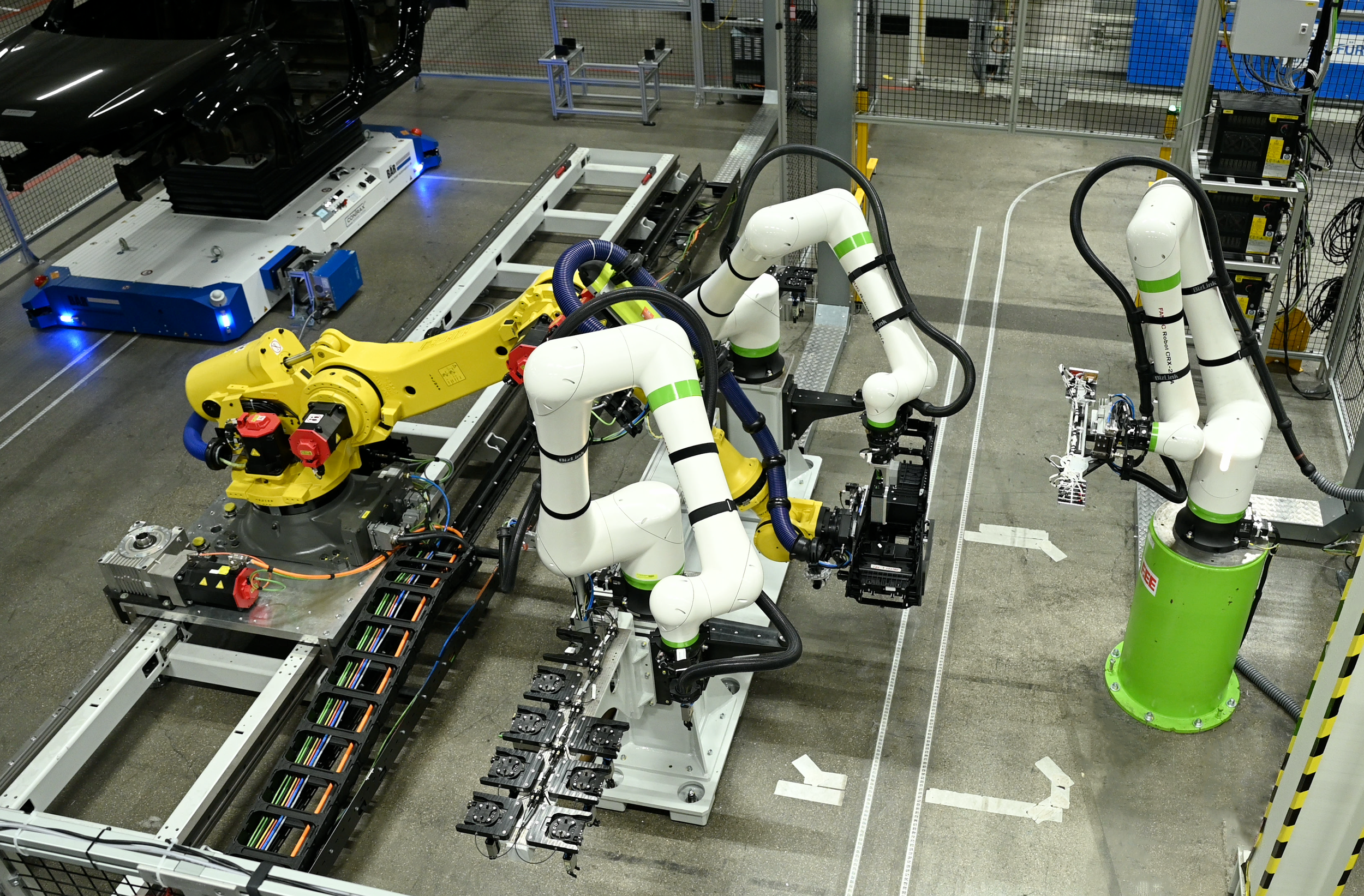
Through the Next2OEM project, Audi works with ten partners at its Ingolstadt headquarters to demonstrate how to digitise and automate wiring loom production and assembly from the supplier through to installation in the factory. Across the industry, manufacturers automate less than 10% of wiring loom production and assembly. The Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy funded a demonstrator in Ingolstadt, and the project team built it to map the full process chain. The demonstrator covers wiring loom production, pre-assembly in the centre console with automation-compatible connectors, and automated installation in the vehicle, with a central system controlling the workflow. Audi expects less logistical effort and much shorter lead times for changes, measured in minutes rather than weeks. The next step will bring the lessons from the demonstrator into large-scale production for future vehicle projects.
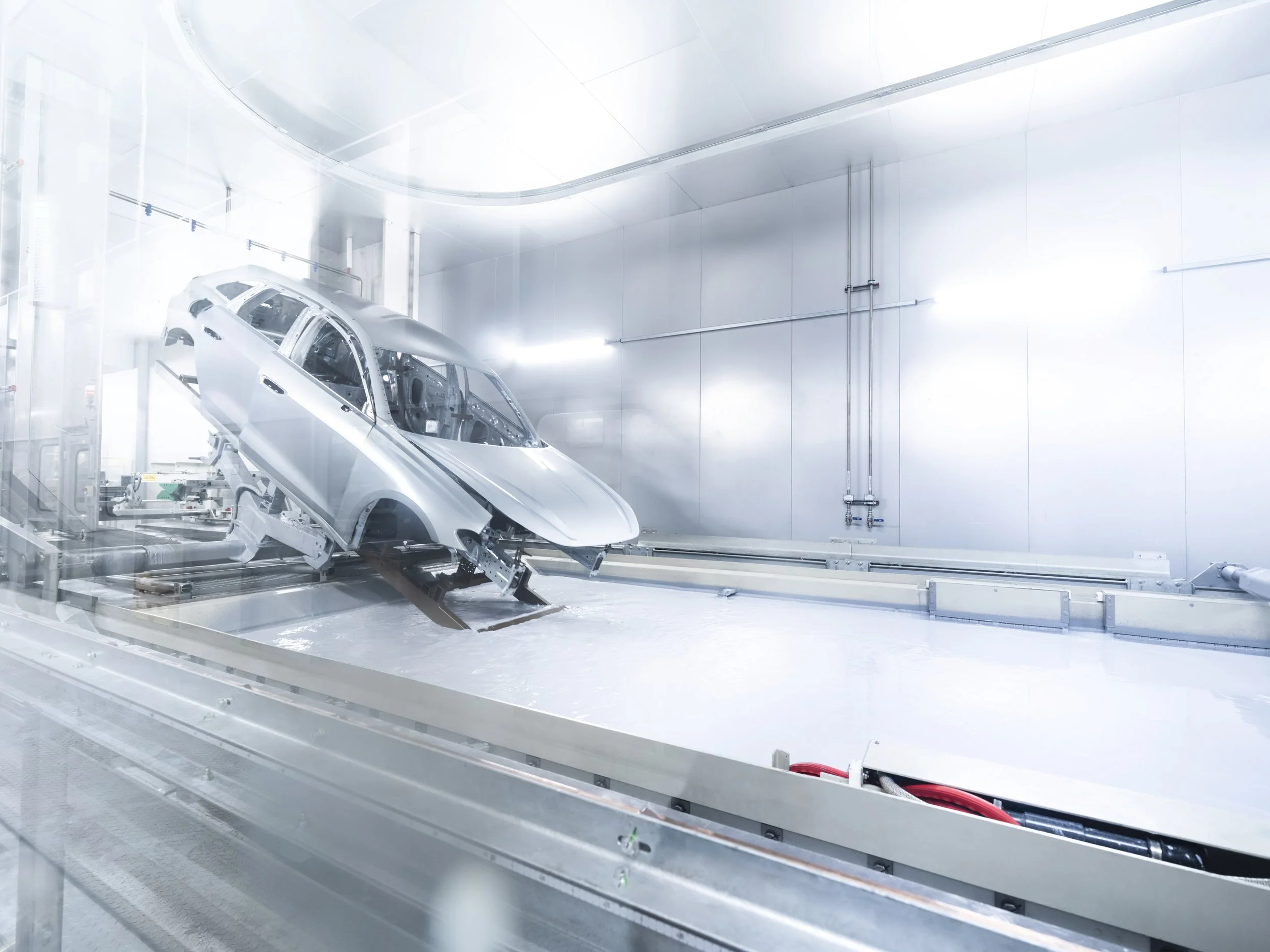
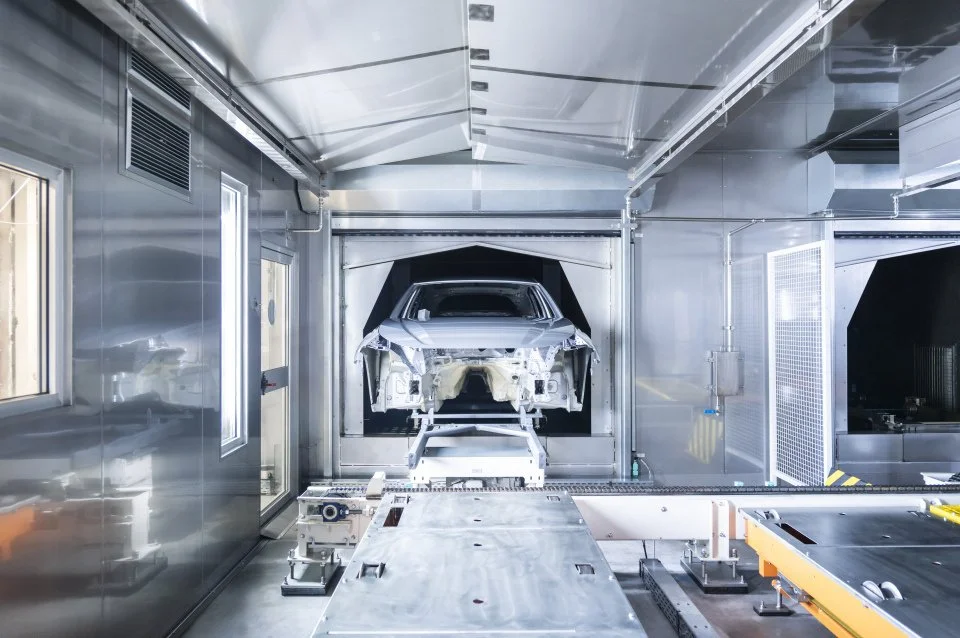
Audi tests its first IPAI cooperation application in series production at Neckarsulm with AI-supported dryer operation in the paint shop. The team based the application on an AI model from another industry, and experts identified Audi’s potential through cooperation and exchange within the IPAI. Engineers now connect various controllers that regulate temperature and air volume in the longitudinal dryer to the AI system. This setup enables the system to respond more quickly to small changes in production line speed and to run the drying process more efficiently. Audi will test energy savings until summer 2026. Audi AG, appliedAI initiative, and CVET GmbH jointly developed the AI-supported system.
Audi supports its data-driven production strategy with in-house expertise and partnerships with industry and science. Around 60 experts in the Audi Production Lab (P-Lab) and the P-Data Factory drive new technologies from the first idea through to series production. Audi also works with Broadcom, Cisco, and Siemens to implement the interaction virtualisation platform, the network, and automation technology as part of EC4P. Audi has also been an active partner in the IPAI in Heilbronn since 2023, and the site is described as a European hotspot for applied AI. These collaborations give Audi access to developments, start-ups, and talent, and accelerate the transfer of innovations into series production. “Together with our partners, we are setting standards for the data-driven production of the future: decisively and responsibly,” said Walker.
Audi sets clear expectations for AI and data use through its Code of Conduct, which binds Audi AG employees, and through a policy statement on artificial intelligence. Audi commits to responsible AI use as a key technology of our time. Audi frames this work around three guiding principles of respect, security, and transparency, which aim to unlock AI potential, protect the company and its employees, and respect user rights.
Across the production network, Audi scales AI in automotive production through shared approaches and cross-plant collaboration. The Audi Hungaria team systematically assesses its value chain digitalisation opportunities, from planning and manufacturing through to quality assurance, and it uses AI to make production processes in Györ, Hungary, more transparent and efficient. At Audi México, management uses the AI-supported “Production Reports” tool to view key figures in real time and make decisions using precise, up-to-date operating data from the San José Chiapa plant.